Every dog owner has watched their furry friend pant heavily after a walk or during a hot day. But when panting becomes excessive or happens at unusual times, it can leave pet parents feeling worried and confused.
Understanding the reasons behind your dog’s panting is crucial for their health and your peace of mind. This blog will explain the most common causes of why does my dog pant so much, from normal behaviors to potential health concerns that require attention.
You’ll learn how to identify when panting is normal versus when it signals a problem, plus practical steps to help your dog feel more comfortable.
What is Normal Panting in Dogs?
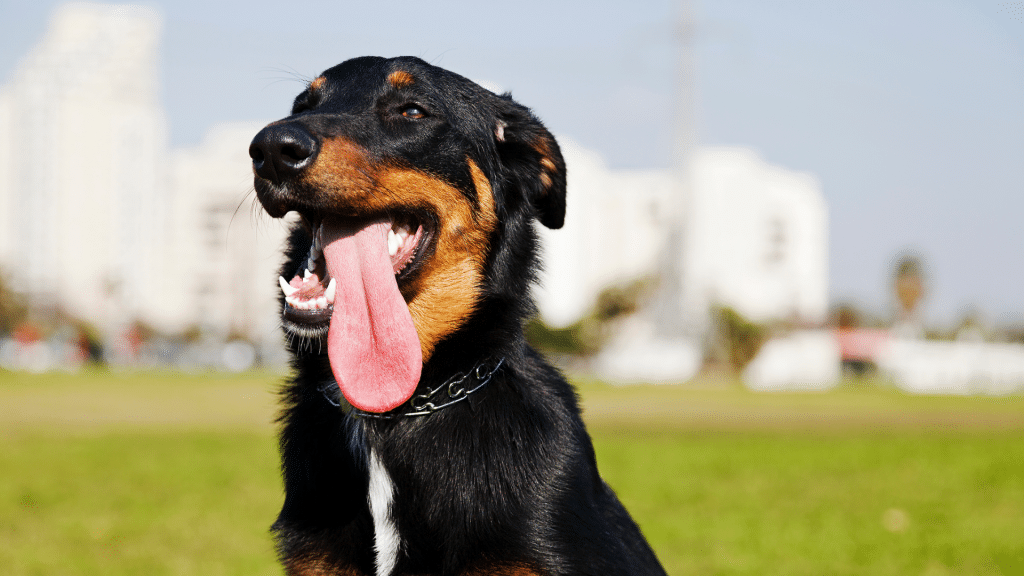
Normal panting is a natural and essential behavior in dogs that helps regulate their body temperature. Unlike humans, dogs cannot sweat effectively over their bodies, so they rely primarily on panting to cool down.
This process involves rapid, shallow breathing with the mouth open and tongue hanging out, which promotes evaporation of moisture in the lungs and mouth, cooling the dog from the inside out.
Normal panting typically occurs after exercise, during hot weather, or when a dog is excited or stressed. It is usually short-lived and accompanied by a relaxed body posture, resolving once the dog cools down or calms
Top Reasons: Why Does My Dog Pant So Much
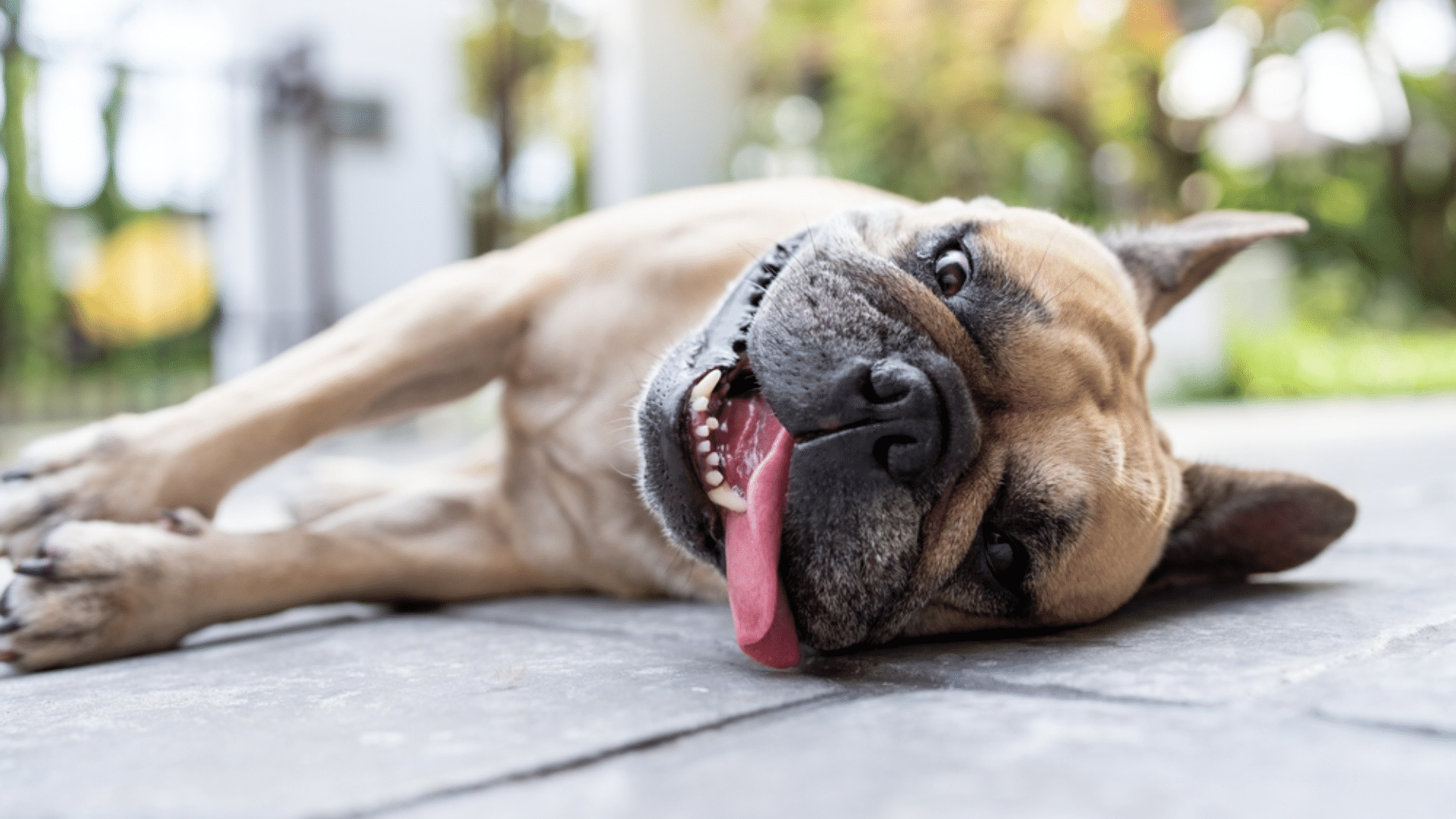

Panting is a normal behavior in dogs, but excessive panting can signal an underlying issue that requires attention. Recognizing the reasons behind your dog’s heavy breathing helps you respond quickly and keep your pet healthy.
Below are the top reasons that give an answer to your question, why does my dog pant so much.
1. Heatstroke or Overheating
Heatstroke is a life-threatening emergency where your dog’s body temperature rises to dangerous levels. Dogs pant to cool themselves, but in hot weather or heat, this may not be enough.
Heavy, persistent panting with restlessness or lethargy, especially after being outdoors, requires urgent veterinary assessment to prevent brain damage or organ failure.
2. Exercise and Overexertion
After play or vigorous activity, dogs naturally pant to help oxygenate their bodies and cool down.
This type of panting is expected and short-lived, but if your dog continues to pant long after exercise or shows signs of exhaustion, it could indicate overexertion or an inability to cool down in hot or humid weather.
3. Pain or Discomfort
Excessive panting can be a sign your dog is in pain, even if no obvious injury is visible. Causes range from arthritis or injury to internal problems. Watch for other signs like limping, whining, or restlessness.
If your dog is panting unusually and appears uncomfortable, prompt veterinary consultation is important to determine the source of pain.
4. Stress, Anxiety, or Excitement
Dogs often pant when experiencing emotional changes such as anxiety during thunderstorms, separation, travel, or excitement.
Panting from stress is usually combined with pacing, trembling, or drooling. Addressing the emotional triggers through training or calming techniques can help reduce this panting.
5. Underlying Medical Conditions
Medical issues like heart disease, respiratory disorders (such as pneumonia or laryngeal paralysis), and endocrine conditions (including Cushing’s syndrome) often manifest as excessive panting. Affected dogs may also have coughing, lethargy, or a swollen abdomen.
Any unexplained, ongoing panting calls for a veterinary diagnosis to rule out these underlying diseases.
6. Obesity
Carrying excess weight puts a strain on your dog’s respiratory and cardiovascular system, causing panting after minimal exertion.
Obese dogs struggle to regulate body temperature, leading to overheating and more frequent panting. Gradual weight management under veterinary supervision can significantly reduce this issue.
7. Allergic Reactions or Toxic Exposure
Acute allergic reactions or accidental poisoning can present with rapid, heavy panting as the body tries to compensate for trouble breathing or internal distress.
Additional signs might include swelling, vomiting, or drooling. If you suspect your dog has ingested something toxic or is having a severe allergic reaction, seek emergency veterinary care immediately.
8. Side Effects from Medication
Certain medications, especially corticosteroids like prednisone, may cause noticeable increases in panting even without other changes in your dog’s environment or activity.
If this coincides with starting a new medication, consult your vet about possible side effects and alternative options.
9. Breed Characteristics
Some dog breeds, particularly brachycephalic (flat-faced) types like Bulldogs and Pugs, are naturally prone to heavier and louder panting because of their anatomy.
This makes them more susceptible to overheating and respiratory distress in warm environments or during activity, necessitating close monitoring.
10. Respiratory Infections or Illnesses
Conditions such as kennel cough, pneumonia, or pressure on windpipes can all lead to difficulties in breathing, causing your dog to pant excessively.
If heavy panting occurs along with coughing, fever, or lethargy, visit your veterinarian for a thorough checkup and appropriate treatment
When to Be Concerned About Your Dog’s Panting
You should be concerned about your dog’s panting when it occurs without obvious triggers such as exercise or heat, or if it is excessive and persistent.
Emergency signs include panting accompanied by pale, blue, or bright red gums, difficulty breathing, collapse, confusion, or disorientation. Sudden heavy panting in a cool environment or at rest can indicate pain, stress, heart or respiratory problems, or heatstroke.
If your dog shows labored breathing, drooling, lethargy, or other behavioral changes, seek immediate veterinary care to address potentially life-threatening conditions.
How to Help Your Dogs Deal with Excessive Panting
Excessive panting in dogs can be alarming, but there are practical steps you can take to help your pet feel more comfortable and safe. Addressing panting early helps prevent more serious health issues and ensures your dog’s well-being. Here are effective ways to help your dog cope with excessive panting:
Offer Fresh Water
Dehydration can cause or worsen panting, especially in warm weather or after exercise. Always provide cool, clean water and encourage your dog to drink.
Maintaining hydration supports a healthy panting response and avoids complications from overheating.
Move to a Cooler Environment
If your dog is panting due to heat, immediately bring them indoors or into the shade to lower body temperature.
You can also use fans, air conditioning, or cool, damp towels on their body to help cool them down quickly. Avoid active play during the hottest parts of the day to prevent heat-related emergencies.
Create a Calm, Quiet Space
Stress and anxiety are common triggers for excessive panting. Take your dog to a quiet area away from loud noises, disturbances, or other stressors. Using familiar items like favorite toys or blankets can help them feel secure. Consider white noise or soft music to further soothe nervous pets.
Try Pheromone Therapy
Dog appeasing pheromones, available in diffusers, sprays, or collars, can help promote a sense of calm for anxious or stressed dogs.
These products mimic natural comforting scents that signal safety, making them useful during thunderstorms, fireworks, or when your dog is home alone.
Gently Comfort and Stay Nearby
Simply staying close and speaking softly can help your dog feel secure, especially during anxious episodes.
Gentle petting or sitting quietly with your pet shows support and reassurance, which may naturally slow excessive panting due to emotional distress.
Limit Physical Activity During Heat or Illness
Restrict vigorous exercise if your dog is prone to overheating or is recovering from illness.
Opt for shorter, slower walks during cooler parts of the day, and monitor your dog for signs of exertion, ensuring their physical activity is appropriate for their health status.
When to Seek Veterinary Help
You should seek veterinary help if your dog’s panting is excessive, persistent, or occurs without an obvious cause, like exercise or heat. Immediate veterinary attention is crucial if panting is accompanied by pale, blue, or bright red gums, difficulty breathing, collapse, disorientation, or weakness.
Sudden heavy panting in a cool environment, continuous drooling, or reluctance to move may indicate serious medical issues such as heatstroke, heart problems, or poisoning.
Early diagnosis and treatment can be lifesaving, so don’t hesitate to contact your veterinarian if you notice these concerning signs.
The Bottom Line
Excessive panting in dogs can stem from various causes, ranging from normal responses to heat and exercise to serious health conditions requiring immediate attention. The key is knowing what to watch for and when to act.
Keep your home cool, provide fresh water, and maintain regular vet checkups to prevent many panting-related issues.
Your dog depends on you to recognize when they need help.
By staying alert to changes in their panting patterns and responding appropriately, you’re ensuring they live a happy, healthy life by your side.