Does your dog growl, snap, or guard their food bowl like it’s their most precious possession?
Food aggression affects nearly 20% of dogs, yet many pet owners don’t know how to address this behavior safely. This protective instinct can escalate quickly and create tension during meal times.
Learning how to stop food aggression in dogs doesn’t require expensive training sessions or harsh methods.
The strategies below will show you exactly how to stop food aggression in dogs using positive reinforcement and patience. Let’s start building better mealtime habits today.
Understanding Food Aggression in Dogs
Food aggression can turn peaceful meal times into stressful situations. Recognizing the signs and understanding the root causes helps pet owners address this behavior effectively.
What is Food Aggression?
Food aggression is a form of resource guarding, in which dogs protect their food from perceived threats. This behavior stems from a dog’s natural instinct to protect valuable resources.
Common signs include growling when someone approaches their bowl, stiffening their body over food, or eating faster when people are nearby.
More serious behaviors involve snarling, snapping, or biting when someone gets too close during meals. Some dogs guard their entire feeding area, while others only react when hands reach toward their bowl.
Why it Happens
Food aggression develops from various factors rooted in survival instincts. In the wild, protecting food meant staying alive. This behavior remains strong in domestic dogs.
Past experiences play a major role. Dogs from shelters, puppy mills, or homes where they competed for food often develop guarding behaviors. Stray dogs who had to fight for meals may carry this anxiety into their new homes. Some breeds show stronger guarding tendencies due to their working backgrounds.
Individual personality also matters. Anxious or insecure dogs are more likely to guard resources than confident ones.
Early Warning Signs to Watch For

Spotting food aggression early makes training much easier. Dogs often show warning signs before the behavior becomes serious.
Subtle Physical and Behavioral Cues
Many dogs display quiet warning signals that owners might miss. Watch for these early signs:
- Freezing over their food bowl when someone approaches
- Fast gulping or wolfing down food suddenly
- Hard staring at people who come near their bowl
- Raised hackles along their neck and back
- Body stiffness and rigid posture
- Turning their back to block access to food
- Moving their bowl to a corner or a hiding spot
Severity Levels of Aggression
Food aggression happens in stages that can help you understand how serious the problem has become.
- Mild: Visual warnings like staring, lip curling, or teeth showing. Low growls or verbal warnings without physical contact.
- Moderate: Lunging toward people or snapping in the air. Dogs make threatening movements but don’t make contact yet.
- Severe: Actual biting, attacking, or chasing people away from the feeding area. This level needs immediate professional help.
Understanding these warning signs helps you address the problem before it gets worse.
How To Stop Food Aggression in Dogs
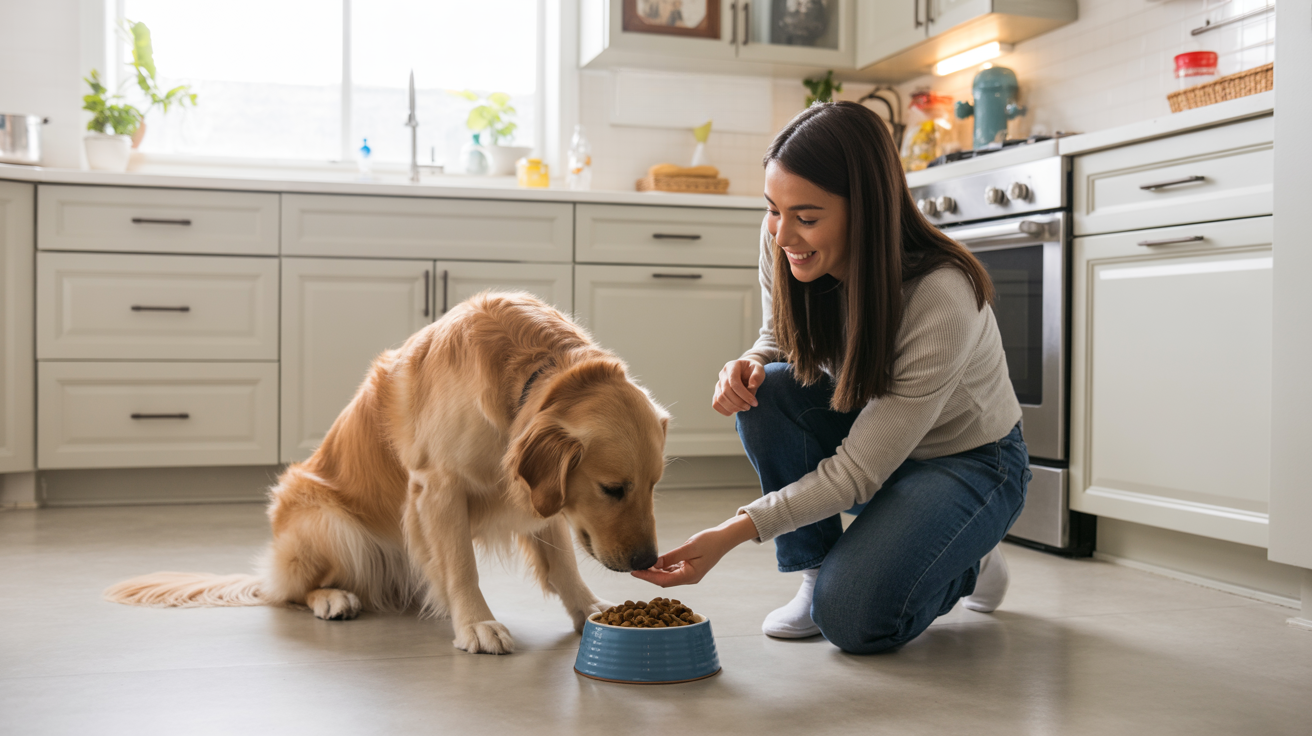

This training method helps dogs learn that people near their food mean good things happen. It would also help you answer the question of how to stop food aggression in dogs. Each step builds trust slowly and safely.
Step 1: Be Present Without Interacting
Start by simply being in the same room while your dog eats. Stand at a comfortable distance where your dog stays relaxed.
Don’t look directly at your dog or make sudden movements during this phase.
Wait for 10 completely relaxed meals before moving forward. If your dog shows tension, increase the distance and give them more time to adjust.
Step 2: Add High-Value Treats
Begin tossing special treats near your dog’s bowl while they eat. Use something your dog loves more than their regular food.
- Start by throwing treats from your safe distance
- Toss treats beside the bowl, not directly at your dog
- Slowly decrease the distance over several training sessions
- Watch for any signs of stress or guarding
Step 3: Talk and Treat Up Close
Move closer while speaking in a calm, happy voice.
Add treats to the bowl or drop them nearby. Use a cheerful but quiet tone and avoid direct eye contact initially. Don’t reach toward the bowl yet. Let your dog finish eating before you leave the area.
This step teaches your dog that your presence means extra good things are coming.
Step 4: Hand Feed Small Portions
Offer high-value treats directly from your hand while your dog eats their regular meal.
- Hold treats at a comfortable distance from the bowl
- Keep sessions short and positive
- Build trust through consistent, calm behavior
Step 5: Touch Without Taking
Gently touch the rim of the bowl while offering a treat with your other hand. Start with very light, brief touches and always give a treat immediately after touching. Watch your dog’s body language carefully and stop if you notice any stiffness or concern.
This step helps your dog understand that hands near their bowl bring rewards.
Step 6: Lift and Replace the Bowl
Carefully lift the bowl a few inches, add a special treat, and then return it immediately.
Start by lifting the bowl just slightly off the ground and adding something extra special to it. Gradually increase the height over time while making sure your dog sees this as a positive experience.
Step 7: Involve the Whole Family
Each family member should repeat the entire sequence from step one. This ensures your dog feels comfortable with everyone around their food.
- Have each family member start from Step 1 and work through all steps
- Don’t assume your dog will accept everyone equally at first
- Children should be supervised during all training sessions
- Maintain consistency in timing and treat rewards across all family members
- Each person should move at the dog’s pace, not rush through steps
Safe Management Techniques at Home
Managing food aggression requires creating a safe environment for both dogs and family members. These techniques help prevent incidents while training is in progress.
| Technique | How to Apply | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Separate Feeding Areas | Feed dogs in different rooms or use baby gates | Removes competition and reduces stress |
| Scheduled Meal Times | Feed at the same time daily, and remove bowls after 20 minutes | Creates routine and prevents lingering food issues |
| Supervise Children | Never leave kids alone with dogs during meals | Prevents accidental triggers and keeps everyone safe |
| Remove High-Value Items | Put away special treats, bones, or toys when not supervised | Reduces opportunities for guarding behavior |
| Create Calm Spaces | Feed in quiet areas away from foot traffic | Helps dogs eat without feeling defensive |
| Use Barriers | Install gates to control access to feeding areas | Gives dogs space while maintaining household flow |
| Monitor Body Language | Watch for tension signs during and after meals | Allows early intervention before problems escalate |
When to Call in A Professional

Some food aggression cases need expert help to ensure everyone’s safety.
Severe aggression that puts family members at risk requires immediate professional intervention. This includes dogs who bite, lunge aggressively, or chase people away from food areas.
Dogs showing little progress after weeks of consistent training may need specialized techniques. Homes with children or multiple pets face extra challenges requiring careful management.
Certified dog trainers with aggression experience offer structured programs and safe techniques, and also help you out with the how to stop food aggression in dogs problem.
Veterinary behaviorists provide the most comprehensive help, combining training with medical support. These specialists can prescribe anti-anxiety medication if needed and address underlying medical issues contributing to food guarding through behavioral therapy sessions.
Finishing It Up
Food aggression doesn’t have to control your household anymore.
The techniques we’ve covered show that learning how to stop food aggression in dogs is possible with patience and consistency. Start with the basic steps and move slowly through each phase.
If your dog shows severe aggression or you feel unsafe, don’t hesitate to contact a professional trainer. They can provide personalized guidance on how to stop food aggression in dogs safely.
What’s your next step? Choose the technique that feels most comfortable for your situation and start today.